
In Sikhism, the Five Ks, also known as Panj Kakar or Five Articles of Faith, are five distinctive symbols that initiated Sikhs are expected to keep as an integral part of their identity and religious practice. These symbols serve as a reminder of the Sikh values and principles.
The "Five Ks" (Panj Kakaar) are five physical articles of faith that are an integral part of the Sikh identity. They were initiated by Guru Gobind Singh Ji, the tenth Sikh Guru, and are considered essential for Sikhs who have undergone the Amrit initiation ceremony (Amrit Sanchar). Each of the Five Ks begins with the letter k ("K") in Punjabi, hence the term "Five Ks." These articles symbolize aSikh's commitment to their faith and serve as external reminders of their spiritual and moral obligations. Here's a brief overview of each of the Five Ks and their significance
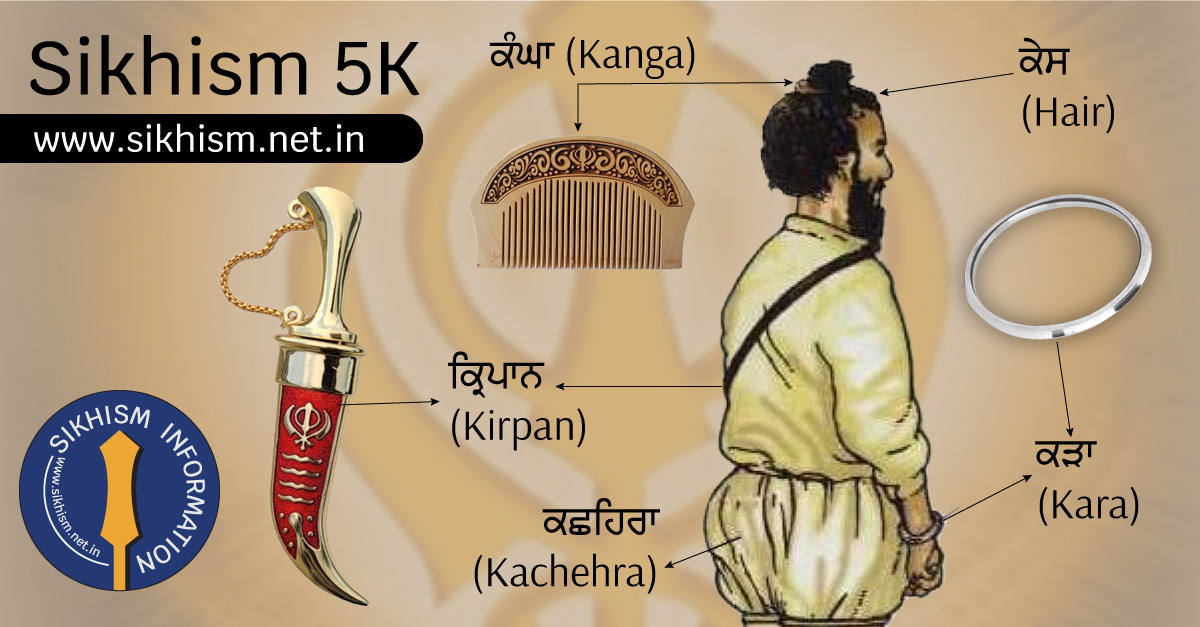
These Five Ks are not merely symbols but embody the core values and principles of Sikhism. They promote a sense of discipline, equality, and devotion among Sikhs. The Five Ks are considered an essential part of a Sikh's external appearance and serve as a reminder of their commitment to the Sikh way of life. By wearing the Five Ks, Sikhs aim to reflect their faith, identity, and readiness to uphold justice and serve humanity. These Five Ks are not just physical objects but carry deep spiritual and symbolic significance for Sikhs. They serve to reinforce the Sikh identity, promote discipline, and remind adherents of their commitment to the teachings of Sikhism. Additionally, the Five Ks help Sikhs maintain a distinct external appearance and serve as a means of expressing their devotion to God and their community.